Gantry Crane Failures and Essential Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Table of Contents
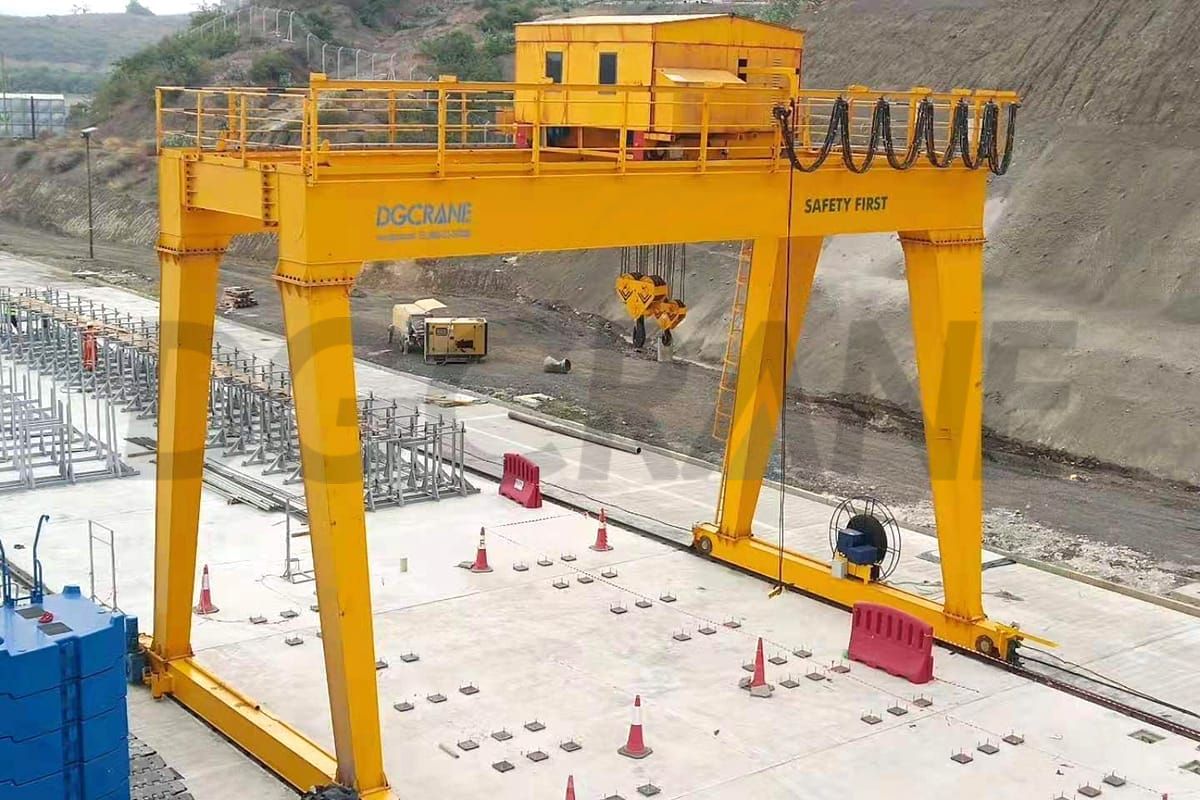

The gantry crane has a complex structure and operates in diverse environments, often leading to various faults during use. These faults not only result in decreased equipment performance but can also lead to safety accidents in severe cases. Effectively analyzing these faults and conducting corresponding research on maintenance and repair technologies is crucial for ensuring stable operation of the equipment and improving production efficiency. Maintenance and repair technologies are key to ensuring the normal operation of gantry cranes.
However, many companies currently do not pay enough attention to this area, leading to frequent fatigue operation of the equipment, which exacerbates the occurrence of faults. Therefore, promoting and deepening research on maintenance and repair technologies is of dual significance for improving both enterprise production efficiency and safety assurance.
Common Faults in Gantry Cranes
Wheel Jamming Fault
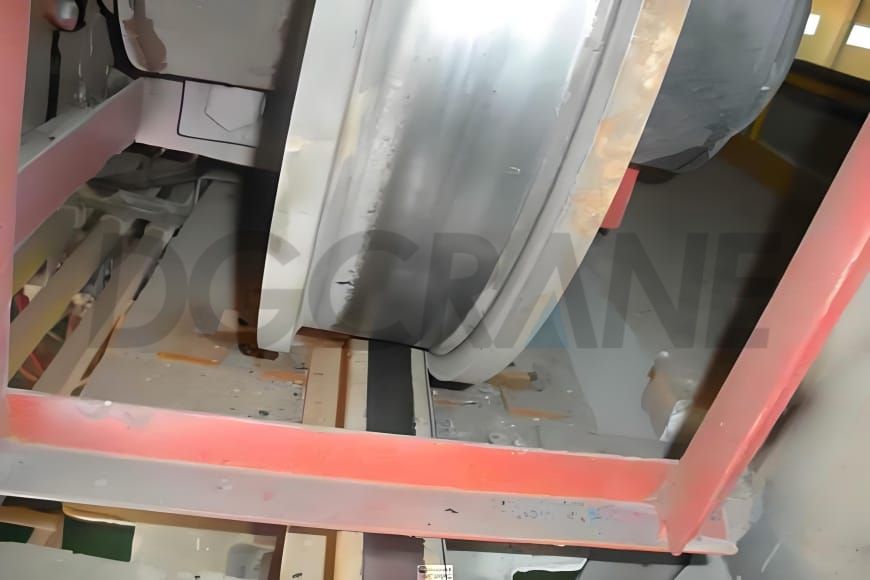

The wheel jamming fault in gantry cranes refers to the situation where the crane’s wheels make abnormal close contact with the track surface during operation, causing the wheels to become stuck on the track and preventing normal movement. This fault may cause the crane to stop functioning and damage the equipment and components.
Wheel jamming can be caused by various factors, including track wear or deformation, wheel wear or damage, faults in the positioning system, or failure to calibrate it, and issues with the lubrication system. This fault needs to be addressed and repaired promptly to ensure the normal operation of the crane.
Gearbox Oil Leaks
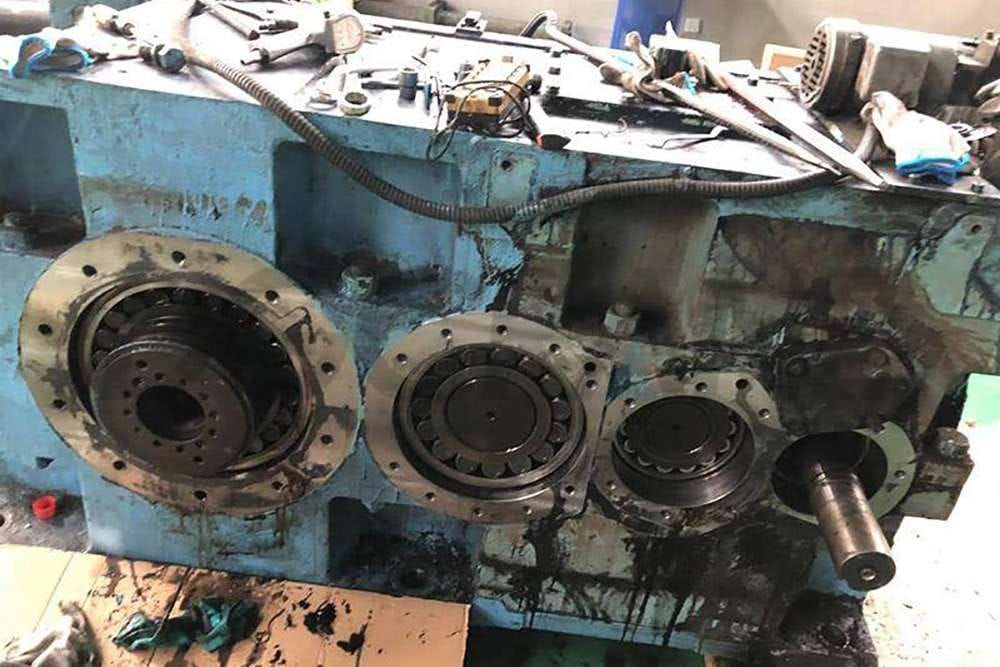

Gearbox oil leaks are one of the common faults in gantry cranes. This fault usually results from a combination of multiple factors. Firstly, improper design of the gearbox may lead to oil leaks. If the gearbox lacks properly set vents or air plugs, internal pressure changes during operation may cause lubrication oil to leak out from gaps. Secondly, if the mating surfaces of the gearbox casing do not meet high precision and tolerance requirements, or if the installation is incorrect, it may cause poor sealing, leading to leaks.
Additionally, poor casting processes that lack necessary heat treatment or aging treatment can lead to deformation and gaps in castings, which also contribute to leakage. Finally, improper installation and maintenance may also result in oil leaks. If the gearbox’s fasteners are not tightened or if the sealing surfaces are not adequately sealed during installation, lubrication oil may leak from the gaps.
Three-Phase AC Motor Faults
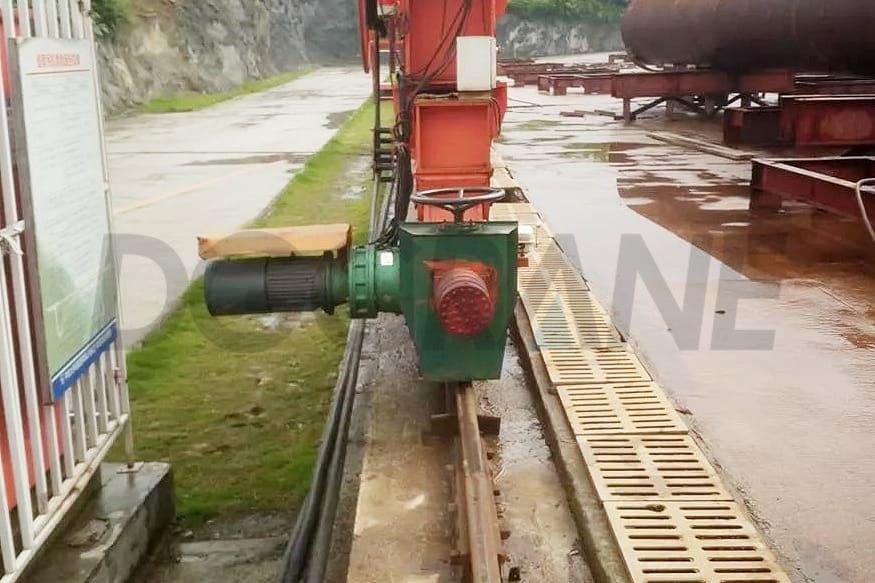

Faults in the three-phase AC motor of a gantry crane are common and can be destructive. These faults are frequent in crane operations. When the motor runs under overload conditions for a prolonged period, excessive heat is generated, which may damage the motor windings' insulation and lead to insulation material aging, potentially causing winding short circuits or open circuits.
Therefore, regular inspection, maintenance, and care of the motor are crucial to ensure reliable operation and prolong its lifespan. Issues such as unstable voltage, phase loss, or the presence of harmonics can interfere with the motor's normal operation. Particularly, phase loss causes the motor to operate in an unbalanced state, generating excess heat and vibration, which accelerates motor damage.
In addition, internal motor components such as windings, bearings, and rotors may fail due to prolonged use or inadequate maintenance, leading to faults such as winding short circuits, bearing wear, and rotor imbalance, which disrupt the motor's normal operation.
Brake Failure
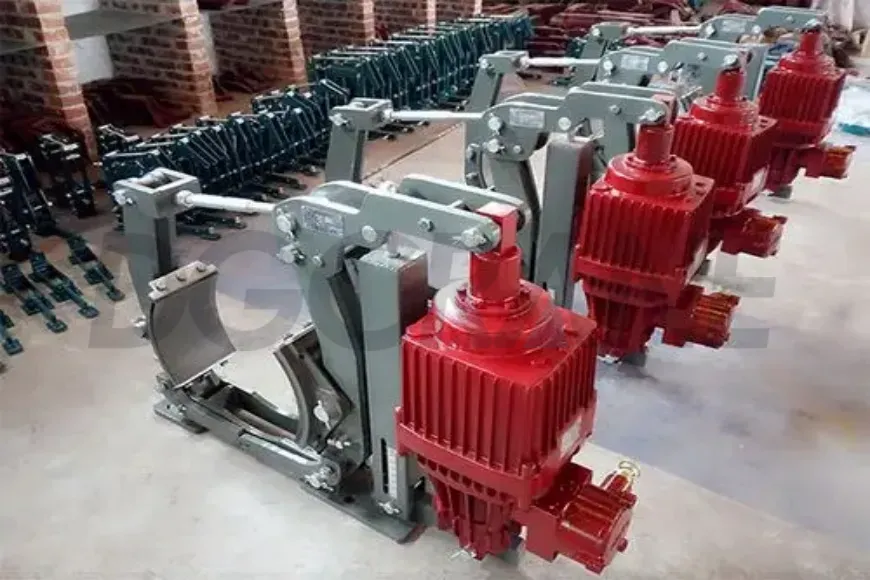

The brake failure in a gantry crane is often caused by prolonged working hours. Continuous operation leads to significant wear inside the brake system, including components like the iron core and hydraulic rods, which gradually lose functionality, reducing the braking torque.
Additionally, the brake's internal circuits may fail, leading to damage to components and coils. If the brake wheel surface accumulates excess dirt and debris, it can also affect the braking system's performance. Poor lubrication of the hydraulic push rods and electromagnetic coils or the presence of excess air can result in the crane’s hinge points getting stuck, which prevents the brake from functioning correctly.
Arm Pivot Point Noises
During frequent operations, the gantry crane is subjected to strong impacts. Continuous force causes the crane's components to age and wear. The pivot points, which serve as crucial connection parts for the crane’s arm, are common sites for faults. During boom movement, if powder-like or granular foreign objects exist within the pivot points, they can hinder the pivot’s normal operation and generate abnormal noise.
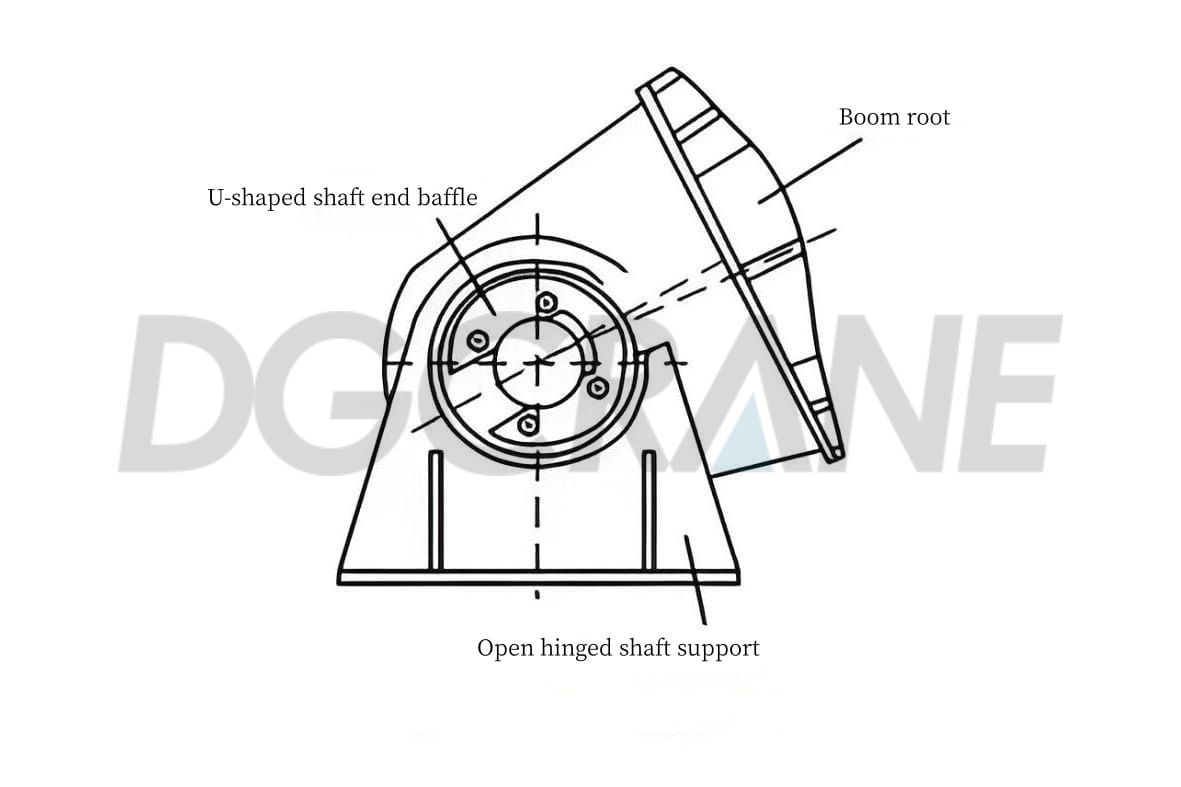
Another common issue is the loosening or breakage of bolts at the end of the shafts. These bolts are essential for securing the shaft ends, and if they become loose or break, the shaft ends may shift or vibrate, thereby affecting the crane’s stable operation. This issue not only causes abnormal noise but also poses a safety risk to the entire crane system. If such pivot point issues are not detected and addressed in time, they may not only affect the normal operation of the crane but also pose hidden safety hazards for production.
Gantry Crane Maintenance and Repair Key Points
Gantry cranes are heavy-duty equipment widely used in various industrial environments, and their stable operation is crucial for the smoothness of production processes. However, due to their complex mechanical structure and operating environments, gantry cranes are prone to various faults. To ensure the proper functioning of the equipment, appropriate maintenance and repairs are essential.
Welding a Certain Thickness of Channel Steel
The Necessity of Welding Channel Steel
Welding a certain thickness of channel steel in a gantry crane is primarily done to increase the structure’s strength and stability. Channel steel is a common metal structural material with a groove-shaped cross-section that can withstand significant bending and shearing forces. It is therefore widely used in various structural projects.
By welding a certain thickness of channel steel in critical areas, the overall strength and stability of the structure are enhanced, improving the gantry crane’s load-bearing capacity and service life. For parts that need to frequently move or vibrate, such as the crane’s track or lifting beams, welding channel steel in appropriate thickness can increase the reliability and stability of the connections, reducing the likelihood of safety incidents caused by loose connections.
Channel Steel Welding Process
First, thoroughly remove any oil, rust, and other impurities from the surface of the channel steel to ensure the welding quality. Next, choose the appropriate thickness of the channel steel, typically 30-40mm steel plates. Then, use welding equipment such as a welding machine, electrodes, gloves, and protective goggles to position the channel steel in the correct place and use the welding machine to connect the two pieces of channel steel.
After welding, carefully check the welds for smoothness and firmness, ensuring that no pores, slag inclusions, or other issues are present. If any defects are found, immediate repairs should be made. Once the welds meet the required standards, remove the fixing tools. During actual operation, adjustments and improvements should be made as necessary to ensure welding quality and safety.
Replenishing Gearbox Lubricating Oil
Replenishing gear lubricating oil in the gantry crane’s gearbox is essential to ensure its normal operation and prolong its service life.
First, ensure that the crane is parked on a flat surface and clean any debris around the gearbox. Prepare the necessary tools, including lubricating oil, an oil drum, and an oil funnel. Open the gearbox oil level check hole, and fully drain the old oil into the prepared oil drum. Make sure the drained oil complies with local environmental regulations and is not disposed of improperly. Use a special cleaning agent or diesel to clean the interior and exterior surfaces of the gearbox, avoiding cleaning agents that may corrode metal. After cleaning, wipe the surface of the gearbox with a clean cloth.
Next, check the oil level by opening the oil filling hole of the gearbox to verify the appropriate oil level. Ensure that the oil level is neither too high nor too low. Based on the gearbox model and specifications, add the appropriate amount of lubricating oil. Be careful not to overfill the gearbox, as this could lead to wastage or overheating.
Finally, check the sealing of the gearbox to ensure there are no oil leaks. If any leaks are found, handle them promptly to avoid impacting the normal operation and lifespan of the gearbox.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance of Three-Phase AC Motors
Inspection and Maintenance Items
Routine maintenance or repair of the three-phase AC motor should always be performed in a power-off state to ensure the safety of both personnel and machinery. The daily maintenance and inspection items for three-phase AC motors are shown in the table below.
| Item | Description | Frequency |
| Power Cut Operation | Ensure power is cut off | Every maintenance |
| Temperature Monitoring | Check component temperature | Immediately after operation |
| Regular Rotation | Rotate when idle for long periods | At least once a month |
| Sound and Odor Observation | Look for abnormal sounds or burning smell | Continuous during operation |
| Vibration Monitoring | Monitor abnormal vibration frequency and amplitude | Continuous during operation |
| Bearing Heat Check | Prevent overheating and oil leakage | Continuous during operation |
| Shell Damage Check | Inspect for damage to the shell | Regular checks (e.g., monthly) |
| Internal Cleaning | Clean oil stains, water drops, etc. | Regular cleaning (e.g., quarterly) |
Inspection and Maintenance Key Points
Proper daily maintenance of three-phase asynchronous motors is essential for ensuring their normal operation. When the gantry crane has been idle for a long period, it is necessary to run the motor once a month and ensure the motor’s heater is in operation to prevent damage to certain parts when starting. During the motor’s operation, closely observe the motor's sound, odor, vibration frequency, and magnitude.
If a burnt smell is detected, stop the operation immediately and inspect the windings and other components to prevent excessive voltage in critical areas. Additionally, pay attention to whether the bearings are overheating during motor operation. When the motor is not running, in addition to rotating it periodically, also check for any damage to the motor casing. Regular internal cleaning of the motor is necessary to prevent water, oil, and other contaminants from entering and ensure the motor remains clean.
Adjusting the Brake Rod Nut
Adjusting the brake rod nut is an essential task in the maintenance and repair of the gantry crane, aimed at ensuring the normal operation of the brake system and extending its lifespan. Before adjusting, check the brake rod nut for any looseness or damage. If any abnormalities are found, promptly address them to ensure the smoothness of the adjustment process. Use tools to rotate the brake rod nut as needed.
During the adjustment, be mindful of the force applied to avoid excessive tightening, which could lead to the rod breaking or the brake system malfunctioning. After the adjustment, ensure the brake rod nut is securely tightened with no signs of loosening, and check the brake system's performance. If the brake performance is inadequate, further adjustment or replacement of relevant components may be necessary. Regular maintenance and inspection of the brake system are required to ensure its proper functioning. In addition to adjusting the rod nut, periodic cleaning of the brake system and inspection for abnormal wear or looseness of its components should be conducted.
Tightening the End Plate Bolts
Tightening the end plate bolts is an important task in the maintenance of the gantry crane. These bolts secure the end plates to prevent displacement or tipping during operation. To prevent issues such as abnormal sounds from the arm’s hinge points, daily inspections should be strengthened, and any loosened end plate bolts should be tightened while cleaning up any debris.
Use appropriate tools, such as a bolt wrench or spanner, to tighten any loose bolts. When tightening, apply moderate force to avoid damaging the bolts or stripping the threads. After tightening all the bolts, check the stability of the end plates, ensuring that they are securely fixed with no significant shaking or displacement. Additionally, record the date of tightening and the operator's information for future maintenance and checks. If abnormal sounds are detected, perform force calculations and analysis, then replace the rolling bearings as needed.
Experimental Analysis
This experiment aims to evaluate the effectiveness of maintenance techniques applied to gantry cranes by comparing the performance parameters of two gantry cranes subjected to different maintenance levels, verifying the effectiveness of maintenance and repair techniques.
The experiment selected two 100-ton gantry cranes from the National Highway 508 project's beam yard, with a total of nine gantry cranes in the yard. Both cranes were purchased by the company in 2017 from China Railway 16th Bureau Group Beijing Rail Transit Engineering Co., Ltd., and were transferred to the National Highway 508 project in 2020. The equipment management numbers are 1902211204078 and 1902211204079, and the crane models are 100T/10T-45M-16M.
The two cranes were divided into two groups: the experimental group and the control group. The experimental group received comprehensive maintenance and repair, including lubrication of mechanical parts, inspection and replacement of electrical components, and tuning of the control system. The control group did not receive any maintenance or repair.
Performance parameters such as lifting capacity, operation speed, and energy consumption were recorded for both groups before the experiment. The two cranes were monitored continuously for 3 months, and changes in their performance parameters were recorded. The data before and after the experiment were analyzed to evaluate the effect of the maintenance techniques. The comparison data between the two groups is shown in the table below:
| Serial No. | Group | Operating Speed (m/s) | Energy Consumption (kW·h) |
| 1 | Experimental Group (Before) | 1.5 | 10 |
| 2 | Control Group (Before) | 1.5 | 10 |
| 3 | Experimental Group (After) | 1.6 | 8 |
| 4 | Control Group (After) | 1.3 | 12 |
Based on the experimental data, the following conclusions can be drawn:
In terms of operation speed, the experimental group's gantry crane increased by 0.1 m/s, while the control group's speed decreased by 0.2 m/s. This indicates that maintenance and repair help maintain the operation speed of the gantry crane.
Regarding energy consumption, the experimental group's gantry crane reduced consumption by 2 kW·h, while the control group's consumption increased by 2 kW·h. This demonstrates that effective maintenance and repair can reduce the energy consumption of the gantry crane.
Conclusion
As an important piece of industrial equipment, the stable operation of gantry cranes is crucial for production. For common faults, in-depth analysis should be conducted to identify the root causes, enabling effective maintenance and repair. This not only affects the lifespan of the equipment but also impacts production safety and efficiency. The experimental results indicate that the proposed methods for maintenance and repair of the gantry crane yield good results and are effective in improving the performance and efficiency of the equipment.
References
Contact Details
DGCRANE is committed to providing the professional Overhead crane products and relavent service. Exported to Over 100 Countries, 5000+ Customers Choose Us, Worth to be Trusted.
Get In Touch
Fill out your details and someone from our sales team will get back to you within 24 hours!



































































































































